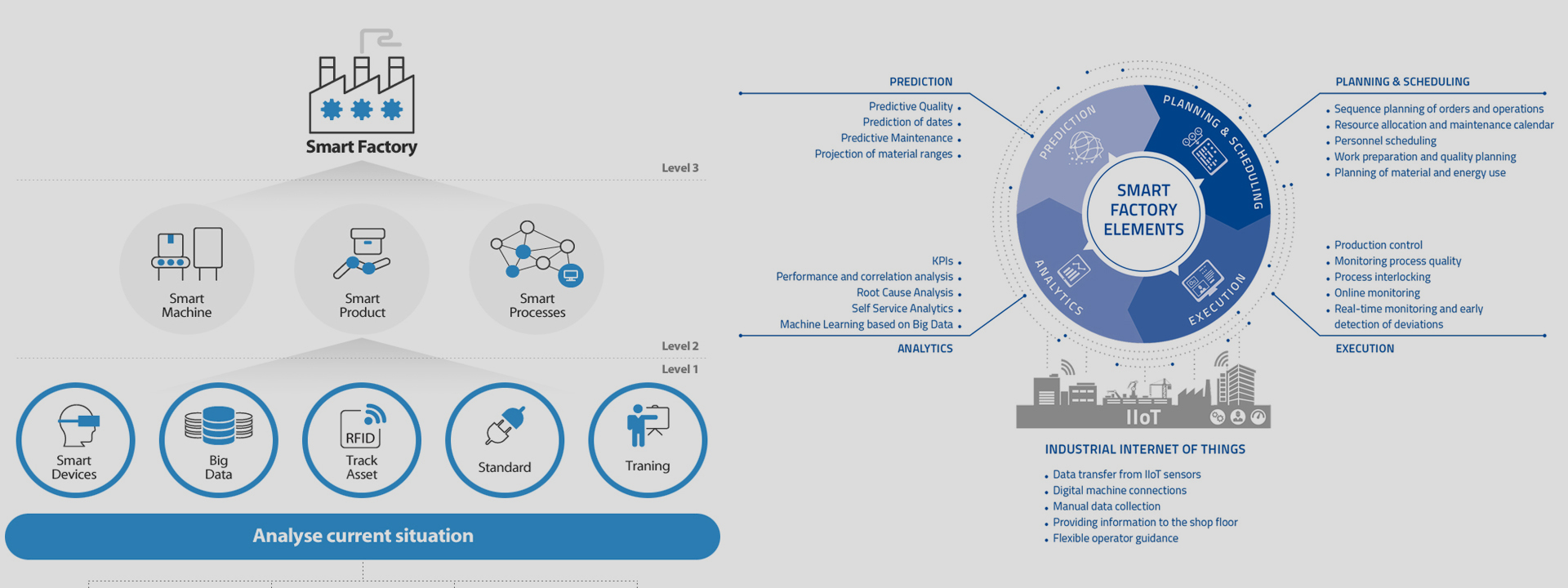
The smart factory represents a leap forward from more traditional automation to a fully connected and flexible system—one that can use a constant stream of data from connected operations and production systems to learn and adapt to new demands. A smart factory is a highly digitized and connected production facility that relies on smart manufacturing. Thought to be the so-called factory of the future and still in its infancy, the concept of the smart factory is considered an important outcome of the fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0. Used by manufacturing companies, a smart factory works by employing technology such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, analytics, big data and the internet of things (IoT) and can run largely autonomously with the ability to self-correct. Yet, the core value of the smart factory still happens within the four walls of the plant. The structure of a smart factory can include a combination of production, information, and communication technologies, with the potential for integration across the entire manufacturing supply chain. All these disparate parts of production can be connected via the IoT (Internet of Things) or other types of advanced integrated circuits (IC’s), which enable sensing, measurement, control, and communication of everything that’s happening throughout the manufacturing process.
We help accelerate smart manufacturing initiatives to drive continuous improvement, knowledge transfer and data-based decision making. We help companies move away from paper and spreadsheets – and guide them digitally through their work processes. We use wireless sensors and cutting-edge IIoT technology to capture, analyse and visualise KPI’s in real-time, so that you can spend more time fixing losses than finding them.
ALWAYS ON! ALWAYS CONNECTED!

Better Decisions in Complex Environments
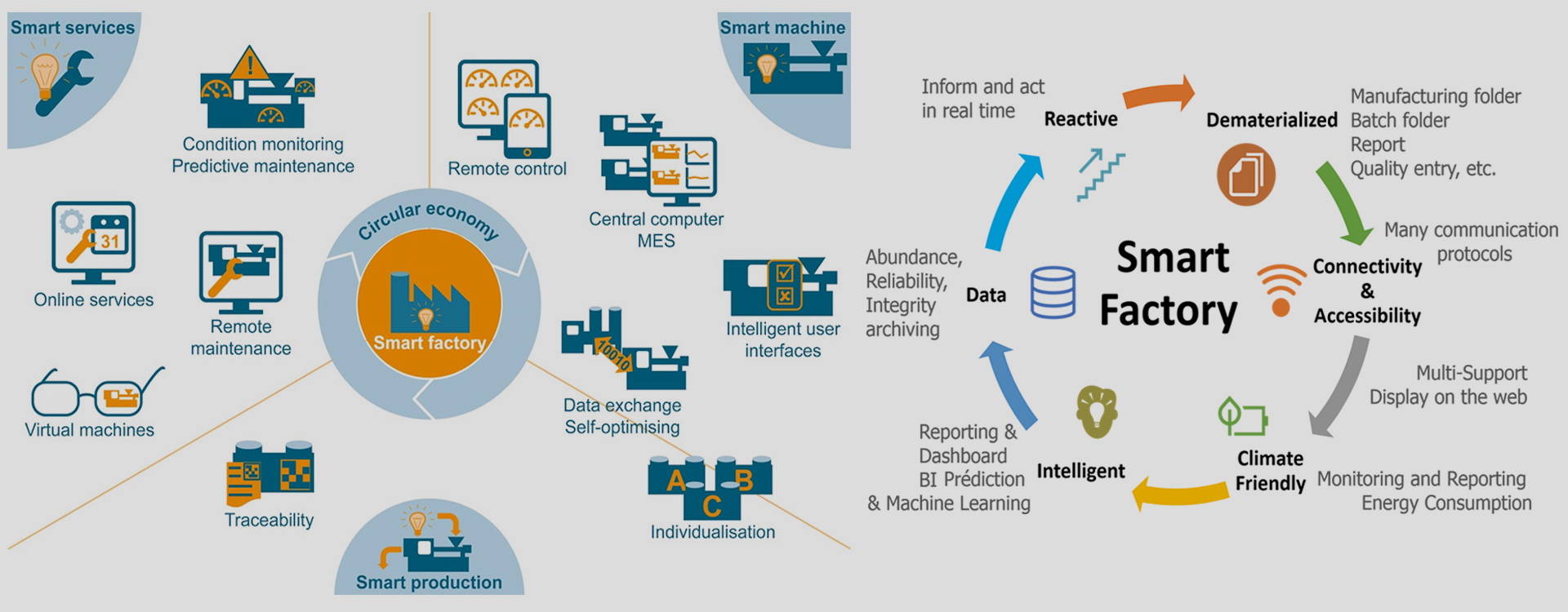
Our Expertise in Smart Factory
Smart Factory Adoption Process
Solution architecture is the process of developing solutions based on predefined processes, guidelines and best practices with the objective that the developed solution fits within the enterprise architecture in terms of information architecture, system portfolios, integration requirements and many more.
In order to achieve our goals, we need to be clear on what the purpose of prioritizing product features is. There are two approaches to prioritizing product features:
The benefits of feedback are manifold.
Reasons Why Factories Need the Smart Factory Platform
Enterprise grade integration mechanisms ensure easy adaptation of existing workflows, business processes and information systems.
Create new processes with ease and add business applications through common interfaces for faster development.
Secure data received from all sources of your IoT ecosystem with state-of-the-art data security systems.
Operate and maintain device and data tasks by automating business processes and save management costs.
Accelerate time to market, reduce cost deployment and maintenance costs of IoT solutions by utilizing interoperable technologies.
Single point for adapting protocols and data models for gathering the information and managing the communications.
Stages of Smart Factory Setup